- It deals with the database design problem
- Normalization process concerns with the transformation of the
conceptual schema (logical data structure) into computer representable form.
- It is a process of restricting data into tables; in order to
ensure efficient & reliable storage & smooth retrieval of data.
Database Schema
A database schema of a database system is its structure
described in a formal language supported by DBMS
Formal Language
- Finite set of strings, symbols or tokens that defines a DBMS
Thus, schemas are the set of formula/rules that specify the
integrity constraints imposed on Database.
Need Of Normalization
As time passes, there will be need for most databases to grow
by adding new attributes and new relations. The data will be used in new ways.
Tuples will be added & deleted.
Information stored will go updation also. New associations
may also be added. In these suitations, the performance of the DB is dependent
upon its design. A bad database design may lead to certain undesirable things
like:
- Repetition of Information
- Inability to report certain information
- Loss of Info.
All this may lead to rewriting of application. Thus
Normalization, helps to attain database design & ensures the efficiency of
database
Advantages of Normalization
- Reduces data redundancies
- It helps in eliminating data anomalies
- It produces controlled redundancies to link tables
Database Integrity
DB contained, data employed by many users. It is important
that the data item & associated relation b/w them not to be destroyed.
The DBMS designed, includes some certain types of checks that
ensures that the data entered in the table conforms to certain rules which in
terms does not violates the original data structure of DB.
Eg. No. of days an emp. Worked in a month can’t exceed the
no. of days in a month.
First Normal Form (1NF)
A relation is in 1NF if and only if all underlying domains of each relation contain atomic(indivisible) values, and the value of each attribute contains only a
single value from that domain.
A
row of data cannot contain repeating group of data i.e each column must have a
unique value. Each row of data must have a unique identifier i.e Primary
key. For example consider a table which is not in
First normal form
- All Key Attributes defined
- No repeating groups in table
- All attributes dependent on Primary Key
Second Normal Form (2NF)
Functional Dependence
In a given table, an attribute Y is said to have a functional
depends on a set of attributes X(X->Y)
If and only if(iif)
Each X value is associated with precisely one Y value
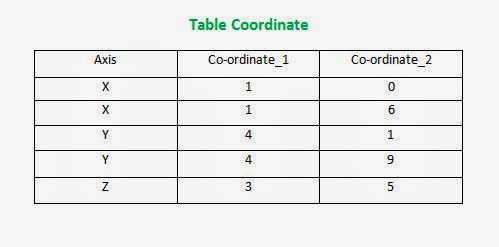
Here, is a Realation(Table), R (Coordinate)
R{Axis, Co-ordinate_1, Co-ordinate_2} are its attributes
(Co-ordinate_1) ------> (Axis) => Co-ordinate_1 is functionally dependent on Axis
(Co-ordinate_2) ------> (Axis) => Co-ordinate_2 is functionally dependent on Axis
(Co-ordinate_1) non-dependent on (Co-ordinate_2)
Partial Dependency refers to the dependency of a non-key (not assigned key constraints) on the portion of the composite-primary-key and not the whole primary key.
Hence,
A relation R is in 2NF if and only if (iif) it is in 1NF and every non-key attribute is fully dependent on the primary key.
R{Axis, Co-ordinate_1, Co-ordinate_2} are its attributes
(Co-ordinate_1) ------> (Axis) => Co-ordinate_1 is functionally dependent on Axis
(Co-ordinate_2) ------> (Axis) => Co-ordinate_2 is functionally dependent on Axis
(Co-ordinate_1) non-dependent on (Co-ordinate_2)
Partial Dependency refers to the dependency of a non-key (not assigned key constraints) on the portion of the composite-primary-key and not the whole primary key.
Hence,
A relation R is in 2NF if and only if (iif) it is in 1NF and every non-key attribute is fully dependent on the primary key.